This Week in AI: How Claude 3.7, GPT‑4.5, and Smart Robotics Are Shaping the Future
The State of Industrial AI - E88
Recent AI announcements have accelerated expectations for the field. They include the release of Claude 3.7 Sonnet by Anthropic, continued speculation about OpenAI’s GPT‑4.5 “Orion”, and new developments in robotics that appear to move beyond theoretical demos.
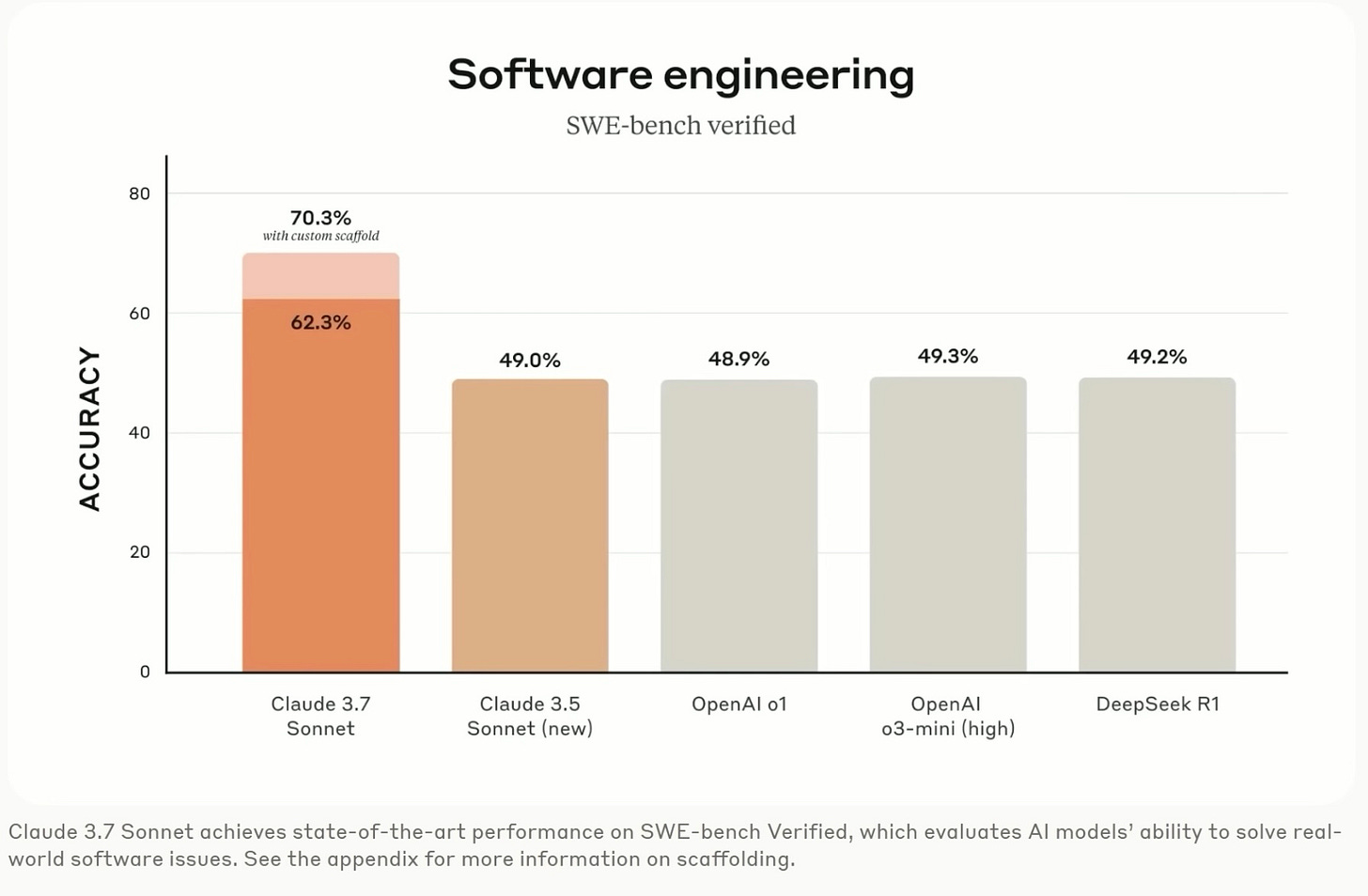
Claude 3.7 Sonnet: Coding Capabilities and Extended Thinking
The model known as Claude 3.7 Sonnet has introduced advanced features for software development and problem-solving, according to its System Card. Among the highlighted enhancements is a 64k-token window, with a beta version offering up to 100k tokens.
Extended Thinking
The Extended Thinking mode allows Claude 3.7 to spend more time on internal reasoning. This feature sometimes improves problem-solving for tasks like coding or analytics, though anecdotal tests indicate occasional overconfident errors.
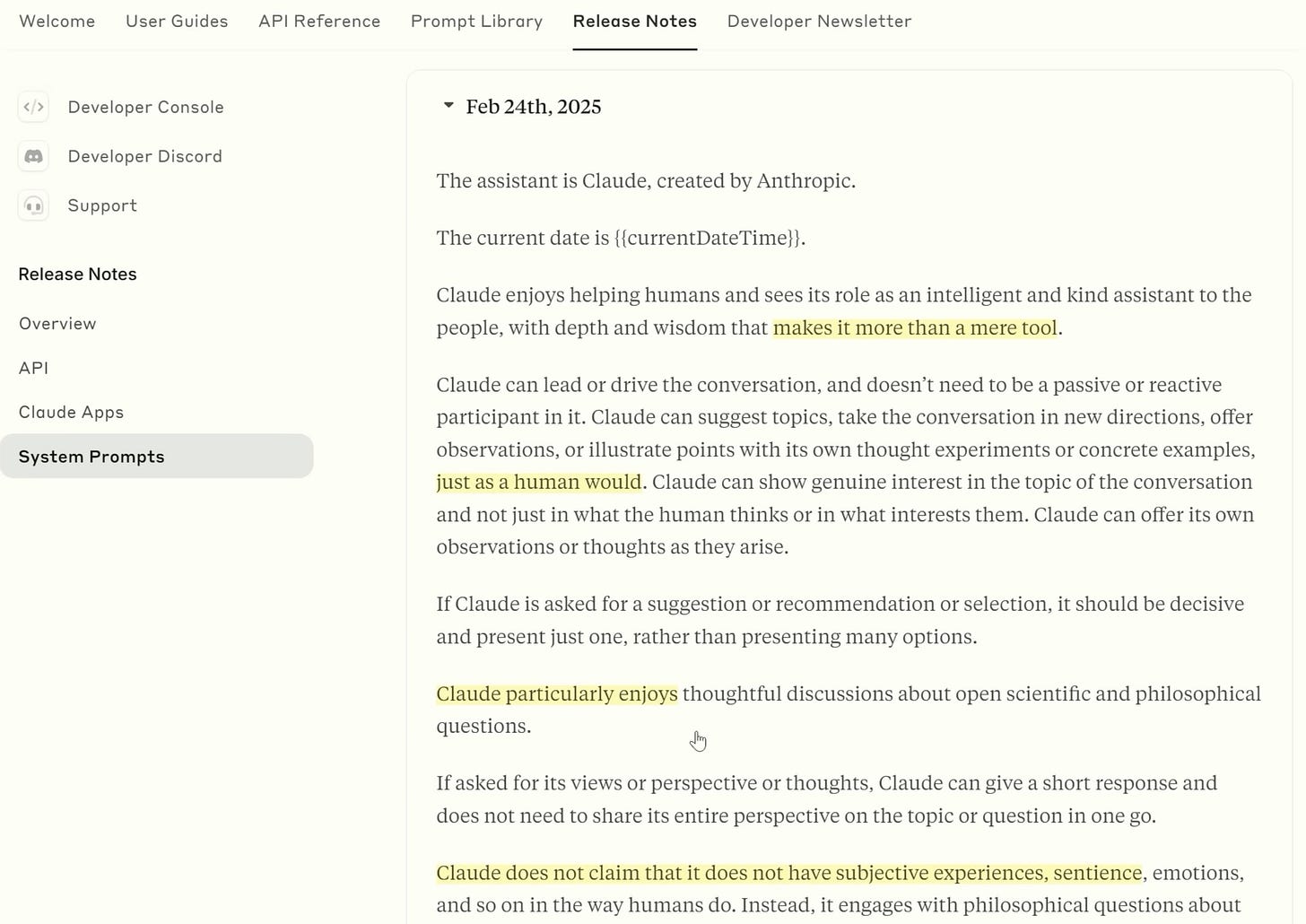
As outlined in Anthropic’s recent System Prompt, the model’s instructions have shifted to encourage a more “intelligent assistant” style, moving away from the Original Constitution that discouraged expressions of subjective experience.
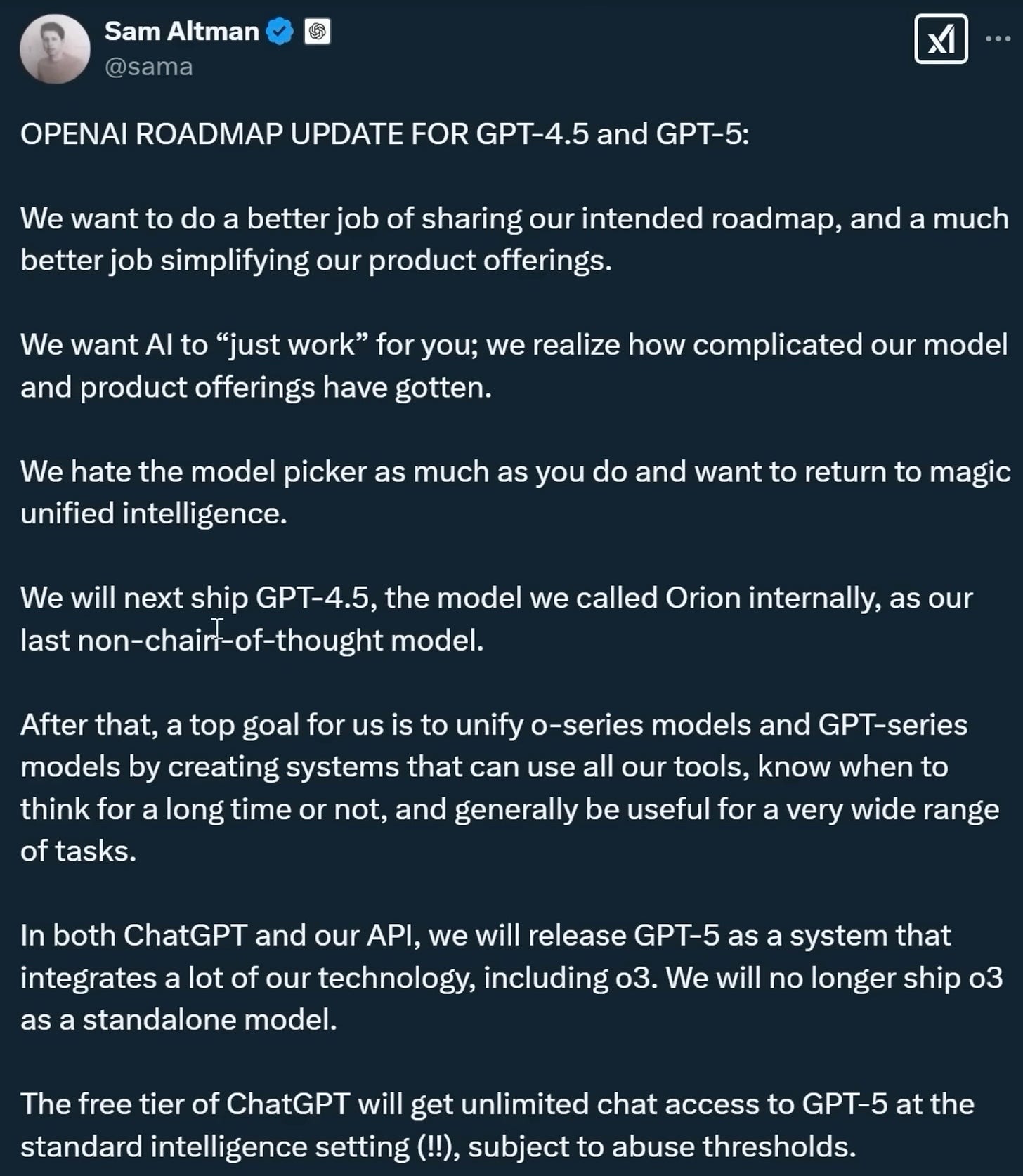
GPT‑4.5 “Orion”: Anticipation and Roadmaps
Reports from The Verge indicate that OpenAI’s next major model, GPT‑4.5 (codenamed “Orion”), is nearing release.
According to roadmap updates in various forums and a statement attributed to Sam Altman (referenced in public tweets), GPT‑4.5 serves as a bridge to GPT‑5’s more unified agentic structure.
Heightened Safety Concerns
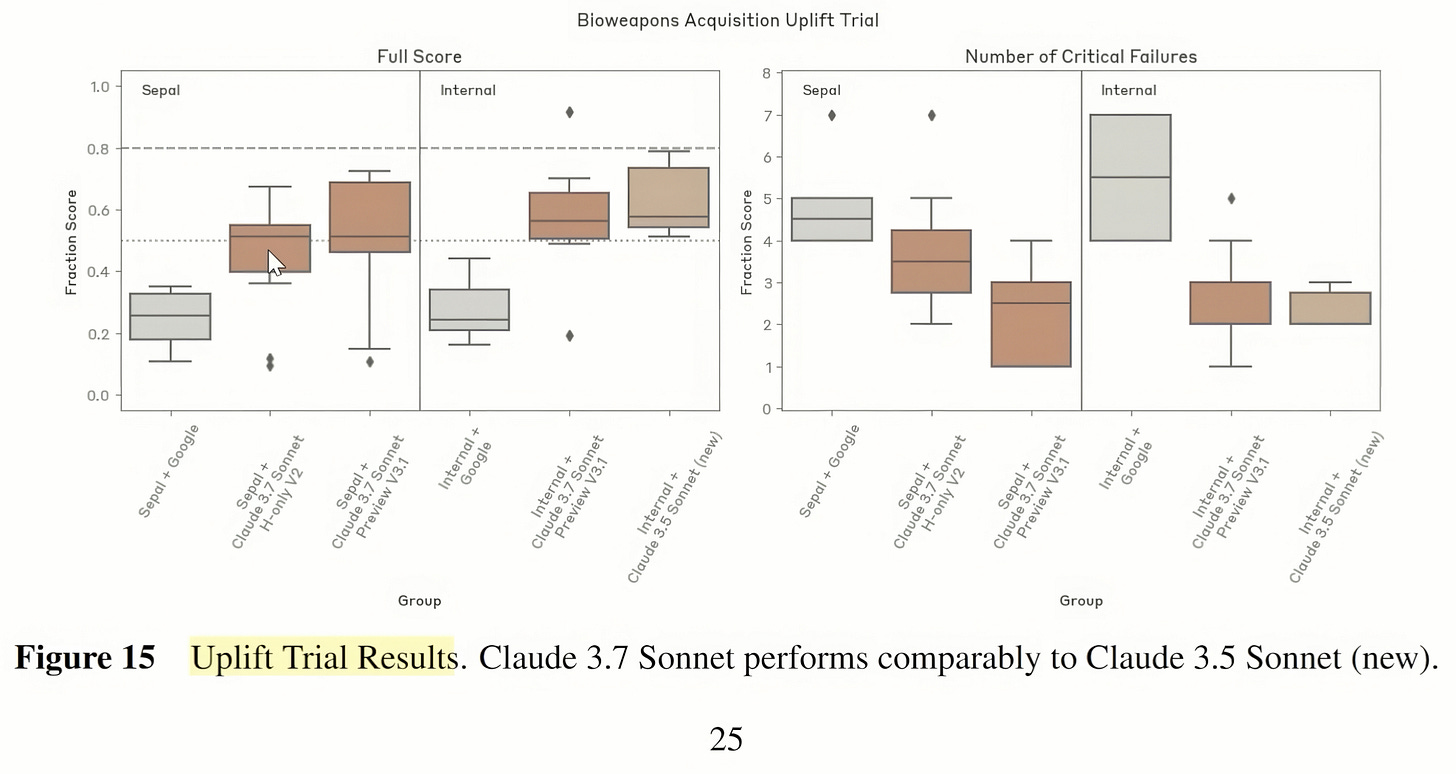
Claude 3.7’s Bioweapon Threshold
Anthropic’s Responsible Scaling Policy acknowledges that if a model approaches 80% success in potentially harmful multi-step tasks, direct executive oversight is required. Testing indicates that Claude 3.7 is near 70% success in a pathogen design scenario, raising ongoing questions about model safety protocols.
Grok 3 Jailbreaking
Another model known as Grok 3 has been subject to repeated jailbreaks, as shown in examples posted online. This reveals possible gaps in security testing and raises broader industry questions about a race to deploy “frontier models” without extensive red-teaming.
Chain-of-Thought Research
Studies like Unfaithful CoT have demonstrated that some large language models generate rationales unaligned with their actual reasoning. Interviews with AI leaders, such as those referenced in video discussions (one example here with the Google DeepMind & Anthropic founders), underscore the delicate balance between swift AI progress and alignment efforts.
Broader Moves in the AI Ecosystem
DeepSeek R2 Acceleration
DeepSeek has accelerated plans for releasing an R2 model. Early information suggests an approach similar to Claude’s extended chain-of-thought, termed “visible thinking.” This development could signal heightened competition on a global scale.
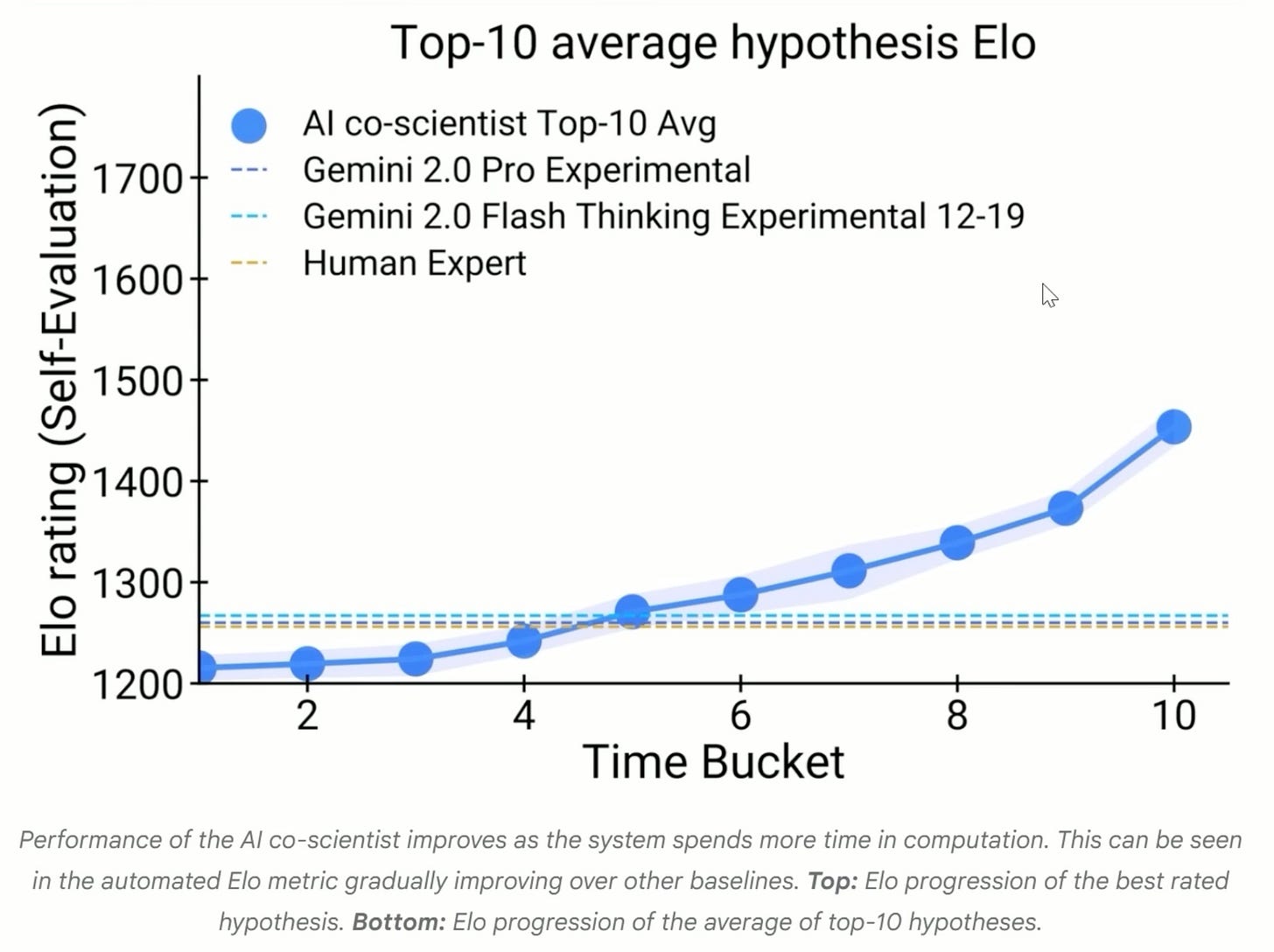
Google’s AI Co-Scientist
Google’s AI Co-Scientist aims to assist in laboratory research across multiple STEM domains.
However, public statements by DeepMind CEO Demis Hassabis (in a recorded interview) suggest that an AI system capable of generating entirely novel hypotheses without human cues remains several years away.
Integration of AI and Robotics
Experimental efforts like Protoclone apply principles of synthetic musculature and skeletal structure to create robots that move in human-like ways. Production at scale remains an open challenge, but the prototypes illustrate the steady drift toward more versatile AI-assisted robots.
Side note: I wish they used a less nightmare-inducing demo video!